|
| LOCATION | LAND AREA
| LAND USE | TOPOGRAPHY | SOIL & MINERAL | CLIMATE |
To see Sarangani in the BIMP-EAGA, please click
here.
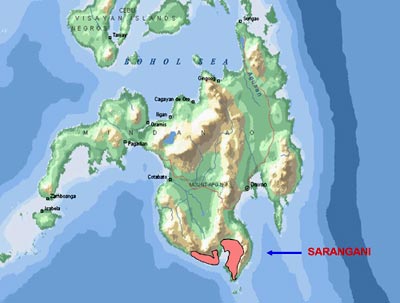
LOCATION
Sarangani, the Mindanao’s front door to BIMP-EAGA, is the
southernmost province in mainland
Mindanao. It is cut midway by General Santos City, giving its two
sections hammock-like shapes that hug the mountains and Sarangani Bay.
Sarangani is surrounded by the Celebes Sea, Sarangani Bay, and the
provinces of South Cotabato, Sultan Kudarat and Davao del Sur.
The province is also the coastal zone of SOCSKSARGEN (South
Cotabato, Sultan Kudarat, Sarangani, General Santos City), one of the
country’s fast growing development clusters.
It has seven municipalities (Alabel, Malapatan, Glan, Malungon,
Maasim, Kiamba, and Maitum) with 140 barangays. Alabel, the provincial
capital, is only 16 kilometers from General Santos City.
With the province’s strategic geographical location, it has great
potential of becoming an industrial zone in Region 12.
LAND AREA
Sarangani has a total land area of 4,100.42 square kilometers.
Among the municipalities comprising the province, Malungon is the
biggest with 896.63 sq. km. followed by Glan. Maitum is the smallest
with only 324.35 sq. km. LAND USE

Part of Sarangani's vast forest lands
About 66 percent of the province’s total land area is a forest
land. Half of this is highly cultivated for corn. These are in
Malungon, Maasim, Malapatan, and Glan.
The province has vast forest cover with 30 percent of the province’s
total forest lands while 37 percent is classified as alienable and
disposable (A & D).
Dense forest cover is located at the western side touching South
Cotabato. The widest is found in the municipality of Kiamba with 87
percent of the municipality’s total forestland. Alabel is noted to
have enormously denuded forestland with 32.49 sq. km. remaining forest
cover.
Grassland forms 19 percent of the total forestland found in Alabel,
and Maasim, mostly idled except for the latter’s pastural
activities.
Two percent of the total forestland figure is croplands and coco
estate distributed throughout the municipalities while Glan, Maitum,
and Malapatan are known for their vast coconut plantations. TOPOGRAPHY

Sarangani's flatlands are ideal for
farming
Flatlands, rolling hills, and mountains characterized Sarangani’s
terrain. The coastal towns of Alabel, Glan, Maasim, Malapatan, Kiamba,
and Maitum are made up of vast stretches of fertile flatlands with
slope ranging from 0 to 8 percent.
Mountains and rolling hills dominate the landscape of Malungon and
the eastern and southern fringes of Sarangani, which border Davao del
Sur and South Cotabato.
The province’s topographic characteristics are attributed to the
presence of Alip Range, Daguma Range, Mt. Parker and Mt. Matutum. Mt.
Busa, the highest peak located within the province has an approximate
elevation of 2,083m above sea level.
SOIL & MINERAL
Soil types of the province range from loam, sandy loam, fine sandy
loam, silty clay loam, clay loam, and mountain clay soil. The province
has also rich deposits of precious metallic and non-metallic minerals
such as gold, copper, iron, silica, limestone, cement lime, coal,
marble, gypsum, phosphate rock, sandstone, white pebbles and guano.
CLIMATE
Northeast monsoon and southwest monsoon are the prevailing wind
directions of Sarangani Province. These are respectively from the
months of November to March and June to October.
There is no distinct dry and wet season in the area. Average
rainfall is 28oC evenly distributed throughout the year. Thus,
Sarangani is considered a typhoon belt area. Annual rainfall is 79.6mm
with 78 percent relative humidity.
April is hottest month while January is coldest. |